Description
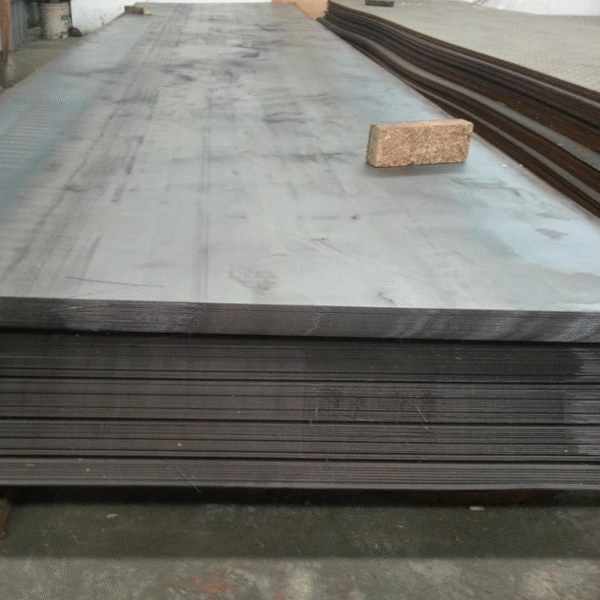
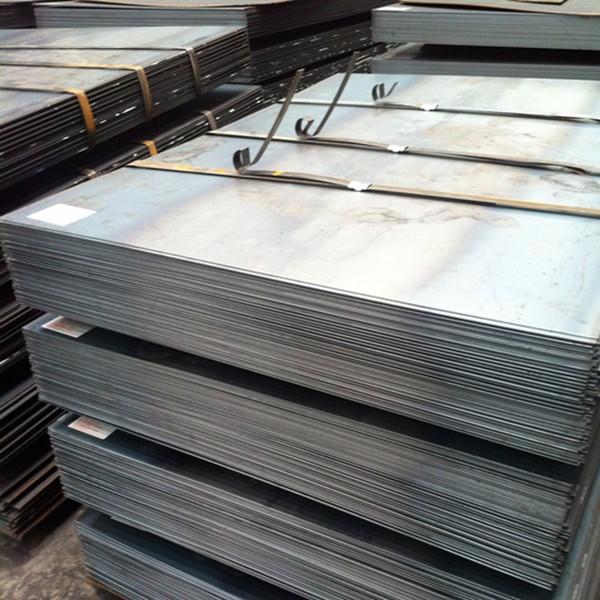
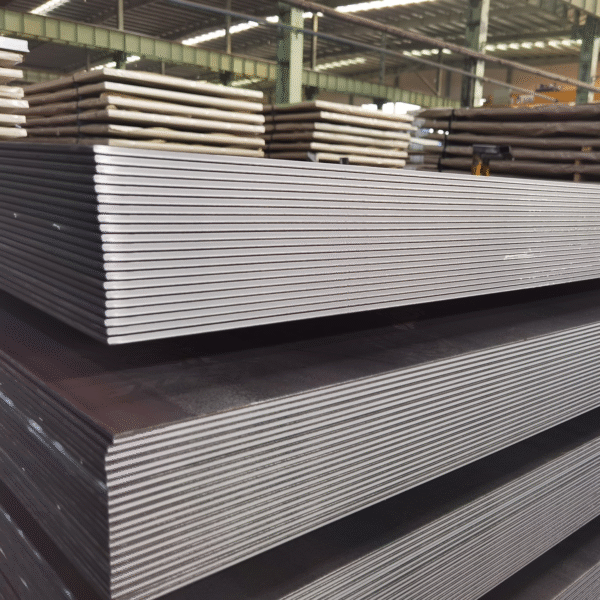
Hot Rolled Plate (Carbon Steel Plates)
Base Material
-
Substrate: Carbon Steel
-
Plate Type: Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Plate
Properties:
-
Strength: Hot-rolled plates are known for their strength, making them suitable for structural applications.
-
Manufacturing Process: Easier to manufacture than cold-rolled plates, with lower production costs.
-
Finish: Typically has a rough, scale-like surface due to the cooling process.
Manufacturing Process
-
Heating: The steel is heated to a temperature above its recrystallisation point.
-
Rolling: The heated steel is passed through rollers to achieve the desired thickness and shape.
-
Cooling: The plate is allowed to cool, either in air or through water quenching.
-
Cutting: After cooling, the plate is cut into the desired length and width.
-
Finishing: The edges may be deburred, and some plates may undergo surface treatments to improve the finish.
Typical Specifications
-
Thickness: 3.0 – 100 mm (depending on grade and application)
-
Width: 1000 – 2500 mm (standard range)
-
Length: Up to 12 meters (depending on customer requirements)
- Grade: ST37 – ST44
Advantages
-
Cost-Effective: Lower production costs compared to cold-rolled plates.
-
Strength: High strength to support structural applications.
-
Versatility: Widely used across different industries due to its reliability.
-
Durability: Resistant to wear and tear, especially in high-impact and high-stress environments.
Applications
-
Construction: Bridges, ships, commercial buildings, municipal infrastructure.
-
Structural Engineering: Brackets, supports, beams, and columns.
-
Manufacturing: Heavy-duty machinery, pressure vessels, tanks, and structural frameworks.
-
Automotive and Transport: Vehicle chassis, body panels, and frames.
Why Choose ERAD Steel?
- Reliable quality and strong steel structure.
- Fast delivery and professional customer support.
- Trusted by clients across Africa, the EU, and the MENA region.
📲 Interested in our Hot Rolled Plate?
Chat directly with our team for pricing and details: